Is Spatial Computing the Next Big Thing?

Today, we are starting a series of articles on "Transforming Industries Through Immersive Technologies." Throughout this series, we'll delve into how immersive technologies are revolutionising various sectors, exploring their potential and transformative impact. Our first article, "Is Spatial Computing the Next Big Thing?" will introduce spatial computing and its foundational concepts. Let's explore the transformative potential of immersive technologies.
Immersive technologies have a rich history. The journey began with the "Sensorama" a multimedia device invented in 1962 by Morton Heilig. This early device aimed to provide an immersive experience through stereoscopic 3D images, audio, vibrations, and even scents.
In the 1960s, Ivan Sutherland and his student Bob Sproull developed the first head-mounted display, laying the groundwork for modern VR.
NASA's Virtual Interactive Environment Workstation (VIEW) was developed in the mid-1980s at NASA's Ames Research Center. This pioneering virtual reality system aimed to create a multisensory, interactive environment that allowed users to explore and interact with both synthesized and real environments.
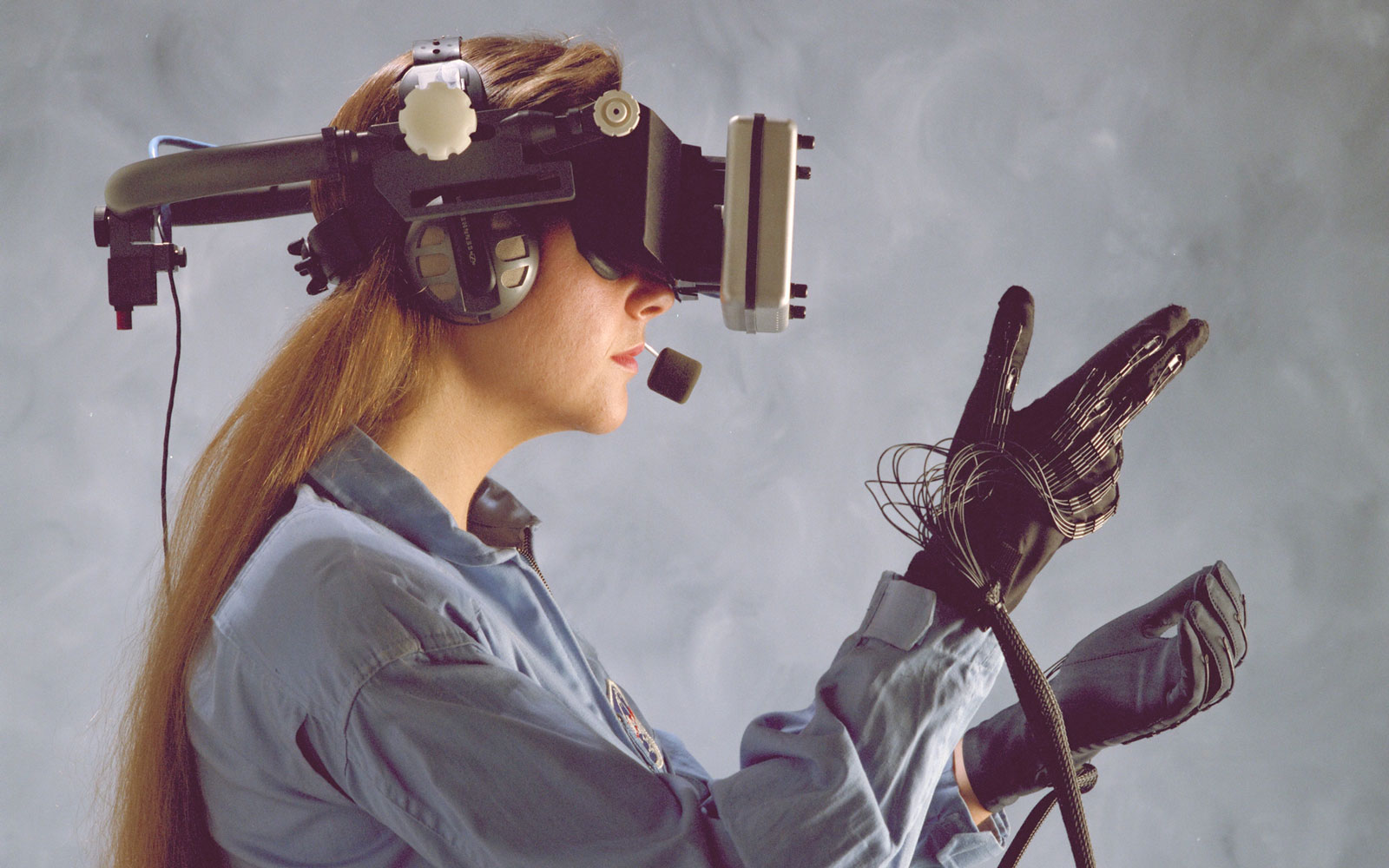

Fig 1:Virtual Environment Reality workstation helmet and gloves, 1989 (Image: NASA)
Spatial computing saw significant advancements in the late 20th and early 21st centuries with the development of devices like Google Glass, Microsoft's HoloLens, and Oculus VR. These technologies expanded the possibilities for immersive experiences, integrating virtual elements into the real world and enhancing the potential for applications in various fields such as gaming, education, and professional training.
We discussed a brief history of spatial computing. Now, let's dive into what spatial computing is.
Spatial Computing refers to the use of digital technologies to interact with and manipulate the physical world in three dimensions. It involves technologies such as AR, VR, MR and XR but extends beyond them to include aspects like 3D mapping, gesture recognition, and spatial awareness. Spatial computing enables the creation of immersive experiences that can understand and respond to the physical environment, enhancing user interactions with digital content in a more natural and intuitive way.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the physical environment with computer-generated information. AR applications often use a camera-equipped device like a smartphone or AR glasses to display virtual elements, such as images, videos, or 3D models, on top of the real-world view.

Fig 2: Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely digital environment, blocking out the physical world. This is typically achieved using a VR headset that provides a 360-degree view of a virtual space. Users can interact with this environment through handheld controllers, allowing for an engaging and immersive experience

Fig 3: Virtual Reality
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed Reality (MR) is a technology that merges elements of both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), allowing digital and physical objects to interact in real-time. Unlike VR, which fully immerses users in a simulated environment, and AR, which overlays digital content onto the real world, MR seamlessly blends virtual objects into the physical world and enables users to interact with both environments simultaneously.
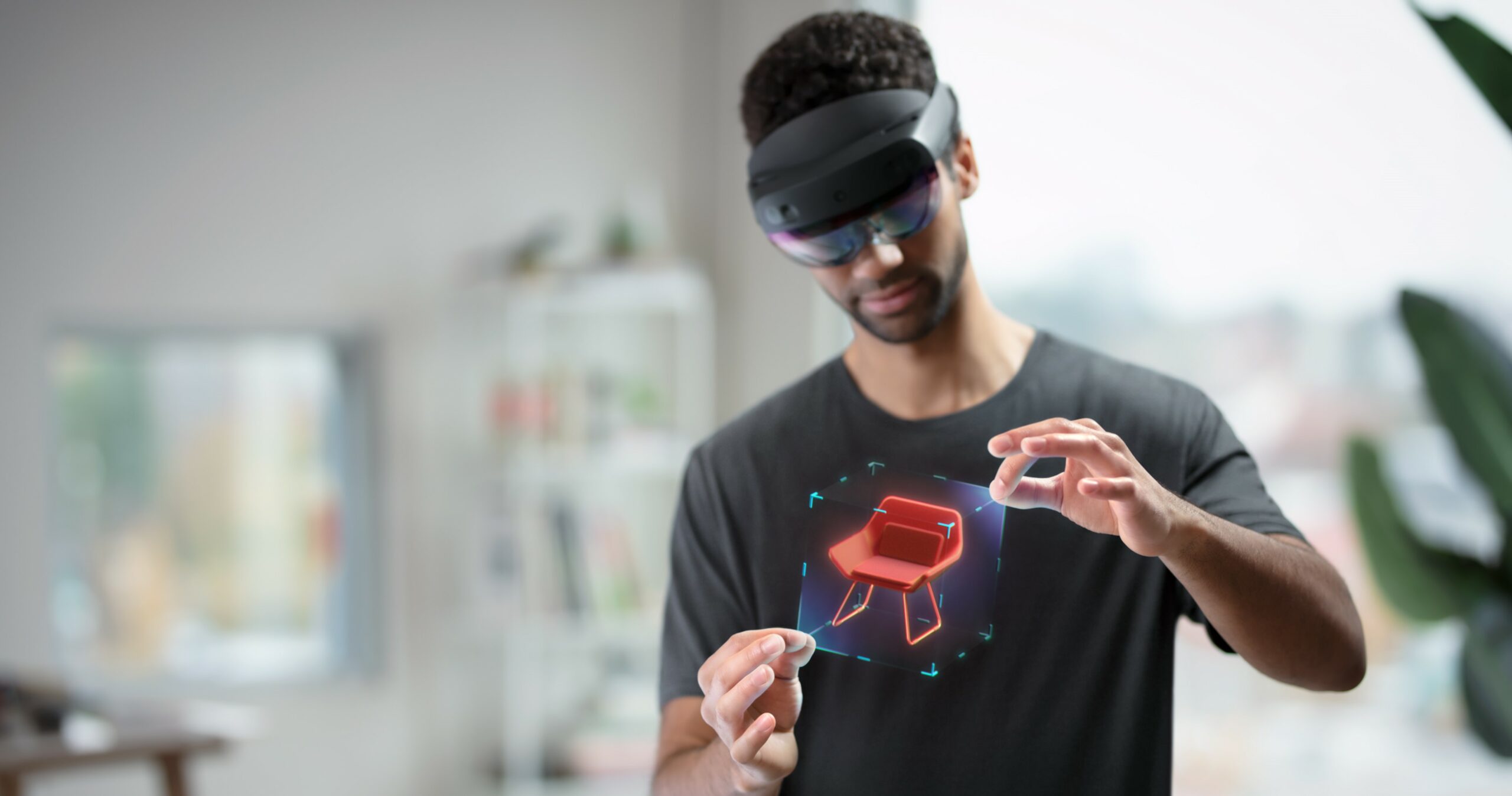

Fig 4: Mixed Reality (Image: Microsoft)
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses AR, VR, and Mixed Reality (MR). It refers to all real-and-virtual combined environments and human-machine interactions generated by computer technology and wearables. XR represents the spectrum of immersive technologies that blend physical and virtual worlds
How Does Spatial Computing Work?
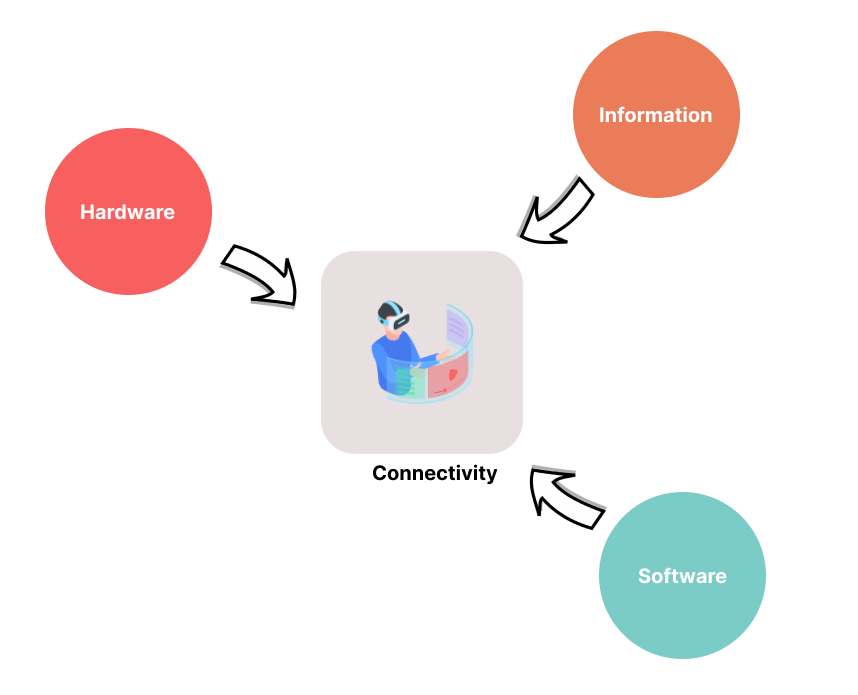
Fig 5: Fundamentals blocks of spatial computing
Spatial computing utilizes a combination of information, hardware, and software to seamlessly integrate digital and physical environments.
Information
Spatial computing relies on a variety of data sources to understand and interact with the physical world.
- Sensor Data: Information from sensors such as cameras, accelerometers, gyroscopes, depth sensors (e.g., LiDAR), and GPS. These sensors provide spatial computing systems with data about the environment and the user's movements.
- User Input: Data from user interactions, including gestures, voice commands, eye tracking, and touch inputs, are used to understand user intent and actions.
Hardware
Spatial computing requires specialized hardware to capture, process, and display information
- Handheld Devices: Smartphones and tablets equipped with AR capabilities (e.g., Apple ARKit, Google ARCore) can display augmented reality content through their cameras and screens.
- Wearables: Devices such as smartwatches and haptic gloves provide additional input and feedback mechanisms for spatial computing experiences.
- Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): Devices like VR headsets (e.g., Oculus Quest, Apple Vision Pro) provide immersive visual experiences by overlaying digital content in the real world or creating entirely virtual environments.
Software
Software frameworks and algorithms are essential for processing data, creating digital content, and managing interactions
- Computer Vision: Algorithms analyze visual data from cameras to detect and recognize objects, track movements, and understand the spatial layout.
- Machine Learning: AI algorithms enhance spatial computing capabilities by improving object recognition, predicting user behavior, and adapting to changing environments.
- Development Platforms: Software development kits (SDKs) and frameworks, such as Unity, Unreal Engine, ARKit, and ARCore, provide tools for developers to create spatial computing applications.
What is Spatial Computing Used For?
Spatial computing has a wide range of applications across various industries, leveraging its ability to blend digital and physical environments for enhanced interactions and experiences. Here are some key uses.
Retail and Marketing
- Virtual Try-Ons: Enables customers to try on clothes, accessories, and makeup virtually.
- Interactive Advertising: Creates engaging and immersive advertising experiences using AR and VR.
Manufacturing and Healthcare
- Design and Prototyping: Allows engineers and designers to visualize and interact with 3D models of products before they are manufactured.
- Surgical Planning and Simulation: Allows surgeons to plan and practice complex procedures using 3D models of patient anatomy.
Entertainment and Gaming
- Immersive Games: Creates highly immersive gaming experiences using VR and AR technologies.
- Virtual Art Galleries and Museums: Creates virtual replicas of physical galleries and museums, allowing visitors to explore exhibits from anywhere in the world.
Workplace Collaboration
- Remote Collaboration: Facilitates remote meetings and collaboration with virtual workspaces where team members can interact with 3D models and shared digital content
Navigation and Mapping
- Enhanced Navigation: Uses AR to provide real-time navigation overlays, showing directions and points of interest on a user’s view of the real world.
Conclusion
In this first part of our series, "Transforming Industries Through Immersive Technologies," we have explored the potential and impact of spatial computing. Spatial computing is revolutionizing the way we interact with both the digital and physical worlds. As businesses and technologies evolve, spatial computing integration will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping our future. Stay tuned for the next article in our series, where we'll dive deeper into a more innovative world of immersive technologies.
Resources and references:
- How virtual reality tricks your brain
- AI + Mixed Reality for the Frontline | Copilot in Dynamics 365 Guides
- 1990: Welcome to VIRTUAL REALITY | Tomorrow's World | Retro Tech | BBC Archive
- A brief history of VR and AR | TechCrunch
- Sensorama - Wikipedia
- A Brief History Of Oculus | TechCrunch
- Google Glass Explorer Edition: Explained!
- A New Continent of Ideas | NASA Spinoff
 16 July 2024
16 July 2024 