Elevating Quality Assurance: Exploring the Test Pyramid’s Benefits and Challenges

In the fast-paced realm of software development, crafting resilient applications that can thrive under real-world pressures is crucial. Enter the Test Pyramid—a concept originally laid out by Mike Cohn in Succeeding with Agile and later refined in Ham Vocke’s insightful article, The Practical Test Pyramid. But this framework is more than just a collection of testing techniques; it’s a strategic blueprint designed to fortify your software against potential failures and performance issues.
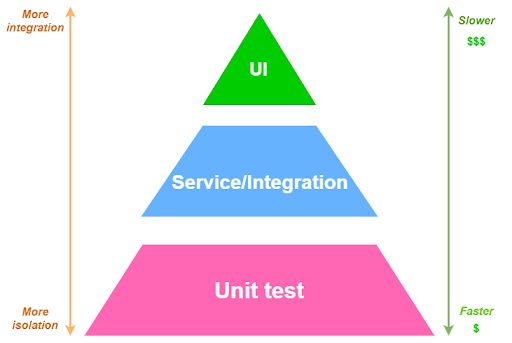
Layers of the Test Pyramid
Unit Tests: The Foundation of Quality
Focus on individual components or functions of the application to ensure they behave as expected in isolation.
Example: Testing a function that calculates the total price in a shopping cart to ensure it correctly adds item prices, applies discounts, and handles empty carts.
Integration Tests: Ensuring Cohesion
Verify the interactions between different components or services, ensuring they work together seamlessly.
Example: Testing the interaction between the shopping cart and an inventory service to confirm that adding items updates the inventory correctly.
UI Tests: Validating User Experience
Simulate user interactions with the application to validate that the UI behaves as intended and provides a seamless user experience.
Example: Automating a test that simulates a user selecting products, adding them to the cart, and completing a purchase to ensure the application responds correctly to user inputs.
Benefits of Test Pyramid
1. Early Bug Detection
Q: How does the Test Pyramid facilitate early bug detection?
A: By prioritizing unit tests, issues can be identified quickly. For instance, in a financial application, unit tests could catch incorrect calculations in a tax computation function before they propagate to reports used for regulatory compliance.
2. Improved Test Efficiency
Q: What makes the testing process more efficient in the Test Pyramid?
A: Unit tests run quickly, allowing developers to receive instant feedback. For example, in an e-commerce platform, unit tests for product search algorithms can run in milliseconds, enabling rapid iterations while adding new features.
3. Maintainability of Test Suites
Q: How does the Test Pyramid enhance the maintainability of test suites?
A: A well-structured test suite makes it easier to update tests. In a microservices environment, if a data model changes, developers can quickly adjust related unit tests without needing to modify extensive E2E tests, streamlining the maintenance process.
4. Risk Mitigation
Q: In what way does the Test Pyramid help mitigate risks in software development?
A: By using integration tests to validate interactions between components. For example, in a ride-sharing application, integration tests can ensure that the mapping service correctly updates ride statuses in real-time, preventing issues during high-demand periods.
5. Better Code Quality
Q: How does the Test Pyramid contribute to better overall code quality?
A: The emphasis on unit testing encourages cleaner code. For instance, in a SaaS platform, implementing unit tests for business logic encourages developers to write modular code, adhering to SOLID principles and facilitating easier future enhancements.
6. Comprehensive Coverage
Q: How does the Test Pyramid ensure comprehensive test coverage?
A: By combining unit tests, integration tests, and UI tests. For instance, in a banking application, unit tests might check individual transaction methods, integration tests could verify correct database updates, and UI tests ensure users can complete transactions without errors.
7. Enhanced Collaboration
Q: How does the Test Pyramid foster collaboration among team members?
A: Clear definitions of test coverage lead to better teamwork. For example, in a healthcare application, developers and testers can work together to establish integration tests that verify compliance with industry regulations, ensuring that all team members understand critical requirements.
8. Cost-Effectiveness
Q: In what way is the Test Pyramid cost-effective for development teams?
A: By reducing reliance on manual testing. For example, an automated testing framework like Selenium can run multiple UI tests simultaneously, cutting down on manual testing hours significantly during release cycles.
9. Facilitates Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Q: How does the Test Pyramid support CI/CD practices?
A: By integrating automated tests into the CI/CD pipeline. For instance, when a developer pushes a new feature to a Git repository, automated unit tests are triggered first, followed by integration and UI tests only if the unit tests pass, ensuring a stable release at every stage.
Challenges of the Software Testing Pyramid
- Test Maintenance: The Overgrown Path
Along their journey, the team discovers that test maintenance is an ongoing battle. As the codebase evolves, tests may become outdated or break due to changes in functionality. This can lead to a growing backlog of failing tests, creating frustration and reducing confidence in the testing suite. - Integration Complexity: The Tangled Web
As they reach the peak, the team encounters the complexity of integrations. In systems with numerous dependencies, testing interactions between components can become a tangled web, making it challenging to isolate issues during integration testing. - Tooling and Frameworks: The Maze of Choices
As the team progresses, they enter a maze of tooling and frameworks. With countless options available for unit testing, integration testing, and UI testing, selecting the right tools can be overwhelming. Each tool has its learning curve and can affect the team’s productivity.
Common Solution: Establishing a Testing Strategy Aligned with the Test Pyramid
To navigate the challenges, teams should adopt an adaptive and collaborative testing strategy. Regularly scheduled reviews of the test suite can help keep tests current, while establishing clear guidelines for integrating and updating dependencies ensures that complexity remains manageable. By standardizing on a set of tools that align with the team's expertise and project requirements, the selection process becomes streamlined, allowing for quicker onboarding and improved productivity. Additionally, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing through documentation and training can empower team members to effectively address challenges, ensuring that the testing framework remains robust and responsive to evolving codebases.
Conclusion
The Test Pyramid is an essential framework that enhances software quality through a balanced testing approach. By prioritizing unit tests at the base, teams can catch issues early and improve efficiency. Despite challenges like test maintenance and integration complexity, adopting a strategic mindset aligned with the Test Pyramid fosters collaboration and continuous improvement. Ultimately, embracing this framework leads to resilient software that meets user expectations and withstands the test of time.