JWT Authentication for Modern Web Applications

Authentication is required to secure user data and to provide access to certain resources that are only accessible to authorized users. One of the most widely adopted solutions being used today to manage authentication in modern applications is JSON Web Tokens. Let us have a detailed discussion on the concept of JWT authentication, how JWTs work, and access and refresh tokens.
A JSON web token is defined as a compact, self-contained way to securely transmit information between two parties as a JSON object. The majority of the usage of JWTs is in authentication and authorization. How?
- Authentication: It helps to determine if the user is who he claims to be identity verification. Every time a user logs in, they get a JWT that states this user is authenticated.
- Authorization: JWTs also control access to resources. Once a user has been authenticated, a JWT can be used to check that a user has permission to access certain resources.
JWT Structure
A JWT consists of three parts:
- Header
- Payload
- Signature
Each of the parts is encoded using Base64Url and joined using periods (.) thus forming a string such as ‘header.payload.signature’
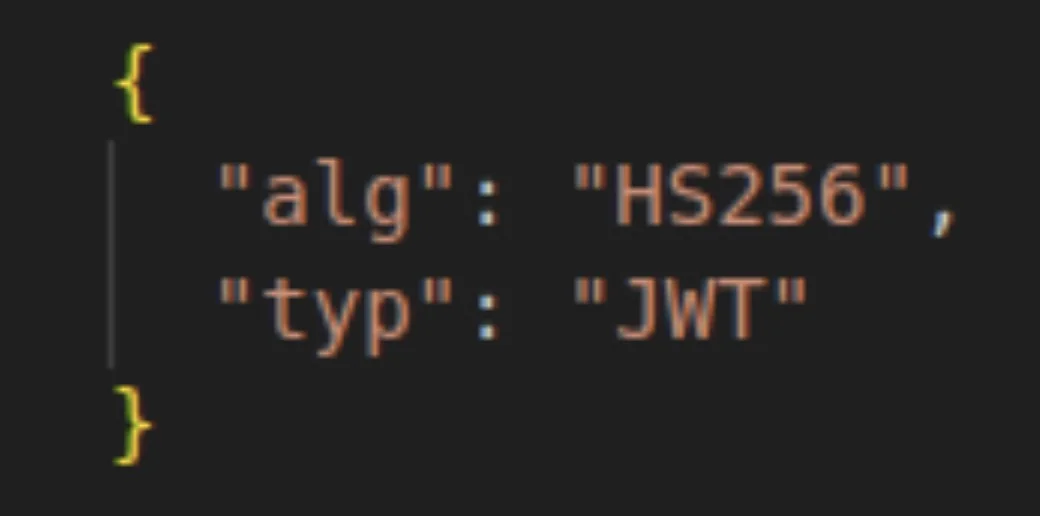
- Header
The header consists of mainly two parts.
- The algorithm that is to be used for signing and encryption principally is HS256 or RS256.
- It defines the token type; that is, JWT.
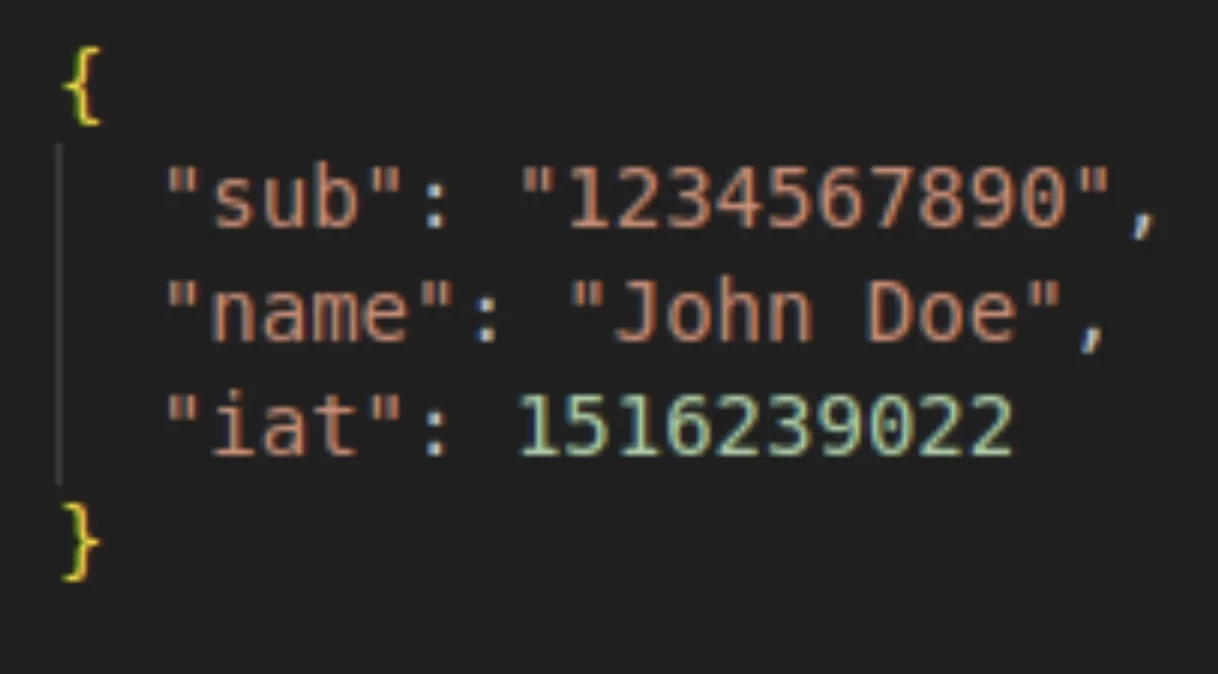
- Payload
The payload is composed of claims. Claims are statements about an entity, usually the user, and some supplementary metadata.
There are 3 types of claims. These include:
Registered Claims: These are pre-defined claims like 'sub' - Subject, 'exp' - Expiration Time, and 'iat' - Issued At. These are recommended by the JWT standard to provide a set of useful, interoperable claims.
Public Claims: These are custom claims. Anybody can define them. They should be collision-resistant. It contains user-defined data, for example, user roles.
Private Claims: These are custom claims designed for sharing information between parties that have agreed to use them. They are used in application-specific requirements.
- Signature
First of all, one should take the encoded header, encoded payload, a secret key, and the algorithm specified in the header. For example, if you are using HMAC SHA256 (HS256), then the signature will be created like this:

The secret key used to sign the JWT forms an integral part of ensuring both the integrity and authenticity of the token. This key should never be shared with the client and only be kept secure on the server.
Within JWT-based authentication, there are two major, different roles for access and refresh tokens on user session management.
Access Token
- An Access Token is used to access protected resources. It is sent with every request to the server in order to prove that the user is authenticated.
- They usually are short-lived; most of them expire within a few minutes to an hour. This limits the damage in case the token is compromised.
- The access token is passed in the Authorization HTTP header with the 'Bearer' scheme.
Refresh Token
- When the current access token expires, the refresh token is used to get a new access token by sending the refresh token to the authentication server to request a new access token.
- Valid for a longer period, often days or weeks, allowing users to stay logged in without frequently re-authenticating. Should be stored securely.
What Happens When an Access Token Expires?
If an access token has expired:
- The request will be rejected by the server if it is either invalid or has expired.
- The client should catch the error and utilize the refresh token to get an access token.
- In the case of the refresh token being either expired or invalid, the user must re-authenticate.
Whenever a refresh token is used to obtain a new access token, a new refresh token is usually generated and returned to the client. The practice provides a rotation of refresh tokens too. Therefore, that adds some more security to them.
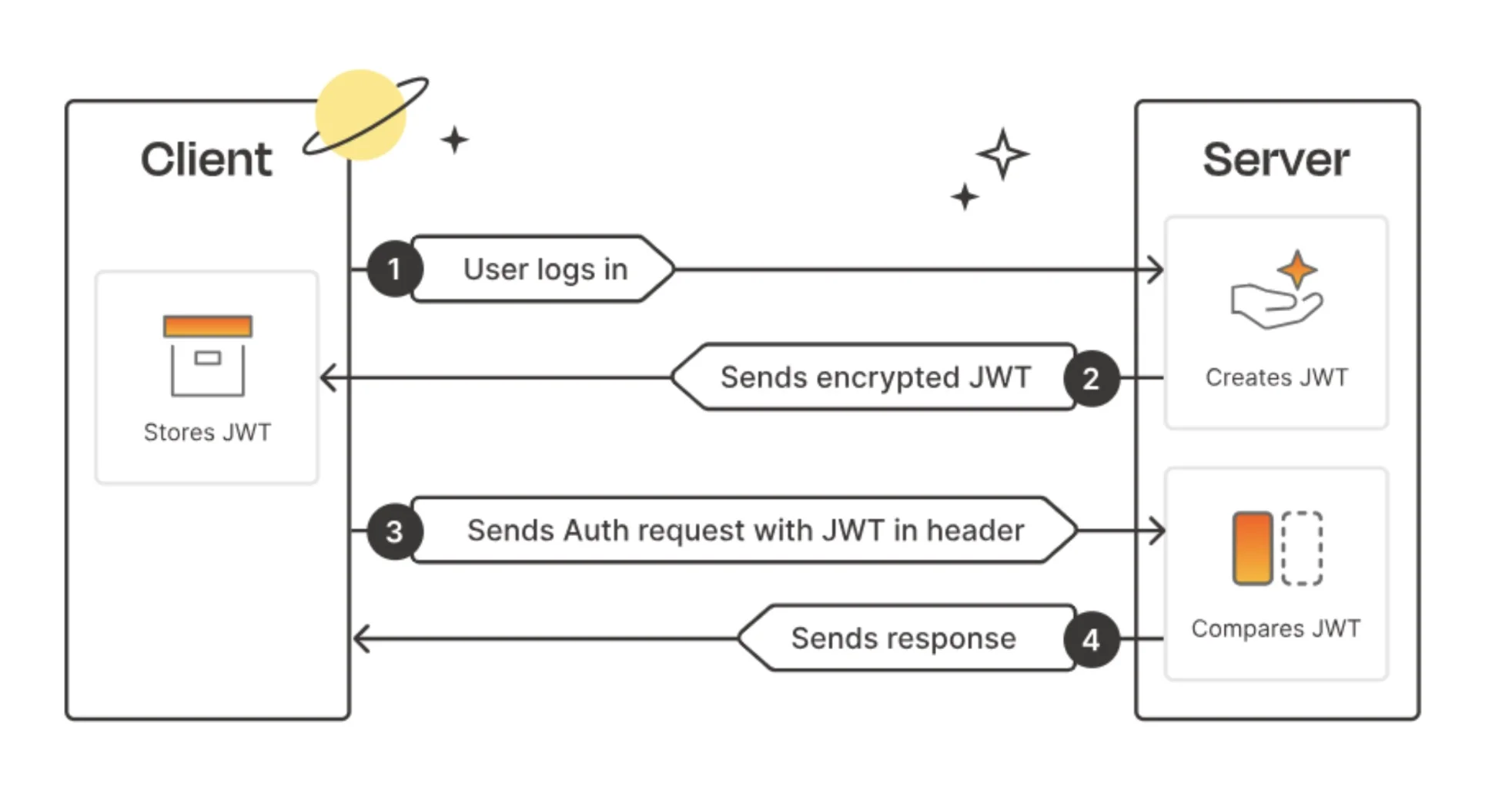
How JWT Authentication Works?
- User Login
The user logs in with his credentials (username and password) through the exposed login endpoint.
- Token Issuance
On successful authentication, JWTs (access token and refresh token) are generated by the server, which comprises the user's information and claims. Again, these tokens will be sent back to the client.
- Token Storage
The client will store the received tokens in local storage or cookies.
-
Authenticated Requests
For subsequent requests, the client includes the access token in the Authorization header using the Bearer schema and sends requests to the server.
-
Token Verification
The server verifies the signature of the token, extracts the payload, and grants access. In case the token is valid, it will process the request; otherwise, it returns an error.
Some Best practices are,
- Keep Your Secret Key Safe
The secret key should not be exposed to any client-side code or be in version control. To manage it, store it as an environment variable or use a secure storage solution.
-
Handle Token Expiration Properly
Include mechanisms that would gracefully handle token expiration. Use short-lived access tokens with long-lived refresh tokens, and provide a clear process by which users could refresh the tokens or re-authenticate when necessary.
-
Use HTTPS
Send JWTs only over HTTPS. This will keep them encrypted during transit and safe from intercepting attackers.