Shift-Left Testing and Shift-Right Testing

Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing are integral concepts in modern software development and quality assurance practices. They emphasize integrating testing activities throughout the software development lifecycle to ensure higher quality, faster releases, and reduced defects. This guide delves into the principles, benefits, implementation strategies, and tools associated with both Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing.
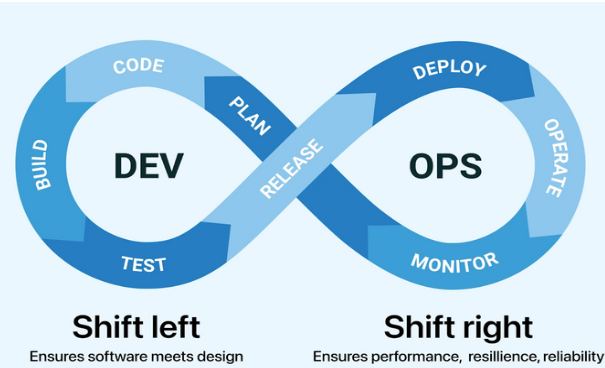
Shift-Left Testing
Shift-Left Testing involves moving testing activities earlier in the software development lifecycle. The goal is to identify and fix defects as soon as possible, thereby reducing the cost and effort required to address issues later in the process.
These are the key principles of Shift-Left Testing:
- Early Involvement: Engaging QA teams from the initial stages of development.
- Continuous Feedback: Providing immediate feedback to developers to correct issues promptly.
- Automation: Implementing automated tests to catch defects early and often.
Early bug detection gives the below benefits:
- Reduced Defects: Catching bugs early minimizes the risk of critical issues in production.
- Cost Savings: Early defect resolution is generally less expensive than fixing bugs post-release.
- Improved Collaboration: Promotes better communication and collaboration between development and QA teams.
These tools can be used for Shift-Left Testing purposes:
- JUnit: For unit testing in Java
- Jenkins: For continuous integration and automated testing
- SonarQube: For static code analysis
Shift-Right Testing
Shift-Right Testing focuses on testing and monitoring activities in the production environment. It aims to ensure that the software continues to function correctly after deployment and to gather real-time user feedback.
These are the key principles of Shift-Right Testing:
- Continuous Monitoring: Observing the application’s performance and behavior in the production environment.
- User Feedback: Collecting and analyzing feedback from end-users to identify potential issues.
- Resilience Testing: Ensuring the system can handle real-world stress and recover from failures.
Shift-Right Testing gives the below benefits.
- Real-World Validation: Testing in production provides insights that pre-release testing cannot capture.
- Improved User Experience: Continuous monitoring helps identify and fix issues that affect users.
- Enhanced System Resilience: Helps ensure the system can handle unexpected conditions and recover gracefully.
Below tools can be used for Shift-Right Testing purposes.
- New Relic: For application performance monitoring
- Splunk: For log analysis and monitoring
- Optimizely: For A/B testing
Combining Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing

By integrating both Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing, organizations can achieve a comprehensive approach to quality assurance. This ensures that quality is built into every stage of the software development lifecycle, from initial design to post-production.
Best Practices:
- Continuous Testing: Implement testing continuously across all phases of development and deployment.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster a culture of collaboration between development, QA, and operations teams.
- Leverage Automation: Use automation extensively to cover both pre-release and post-release testing.
Conclusion
Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing represent a paradigm shift in how quality assurance is approached in modern software development. By integrating testing activities throughout the development lifecycle, organizations can achieve higher-quality software, faster release cycles, and a better overall user experience. Adopting these practices requires a commitment to continuous improvement, collaboration, and the right set of tools and strategies.