How to adopt UX process to Software projects

What is UI & UX
UI (User Interface) Design:
User Interface (UI) design focuses on creating visually appealing and functional interfaces that users interact with directly. UI designers are concerned with the look, feel, and presentation of the product or service. This includes elements such as:
- Visual Design: Designing the aesthetics of the interface including layout, colors, typography, and iconography to create a visually cohesive and attractive design.
- Interactive Design: Designing interactive elements such as buttons, menus, forms, and other controls that users use to navigate and interact with the product.
UI design is more focused on the tangible and visual aspects of the interface that users directly engage with. It involves creating designs that are not only visually appealing but also functional and user-friendly.
UX (User Experience) Design:
User Experience (UX) design is a broader discipline that encompasses all aspects of the user's interaction with a product or service. It's about understanding and improving the overall experience a user has, including their emotions, perceptions, and behaviors before, during, and after their interaction. This includes:
- User Research: Conducting research to understand user needs, behaviors, and motivations through methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
- User Journey Mapping: Mapping out the entire experience a user goes through, from initial awareness to post-interaction follow-up, to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- Prototyping and Testing: Creating prototypes or wireframes to test and iterate on design ideas, gathering feedback from users to refine and enhance the user experience.
UX design is more about the holistic experience and how users perceive and interact with a product or service. It involves ensuring that the product not only looks good but also functions intuitively and effectively to meet user needs and expectations.It doesn't always have to be applicable to software apps .This applies to everything.
Design Thinking Process

Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that emphasizes a human-centered approach to innovation and creativity.It's a non-linear, iterative process that helps teams tackle complex challenges by understanding users' needs, challenging assumptions, and generating innovative solutions. The end goal of the design thinking process is to create solutions that are desirable, feasible, and viable in the real world.
Design thinking is widely recognized as an effective approach to problem-solving across various industries, from technology and healthcare to education and beyond. By embracing the principles of design thinking, teams can create meaningful solutions that address real-world challenges and deliver value to users.
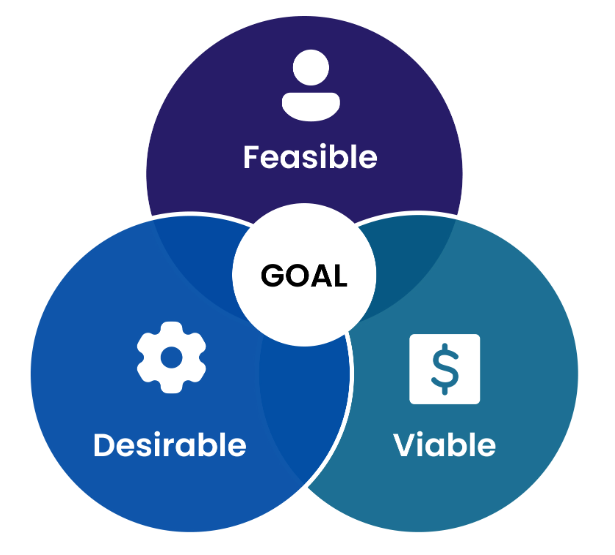
Three lenses of design thinking
Right process for the right project

- Starting a Product from Scratch:
- Revamping or Improving the UX of an Existing Product:
- Adding a New Feature to an Existing Product:
When starting a product from scratch, it's essential to lay a strong foundation that aligns with the needs of your target audience and the goals of your business.
When revamping or improving the user experience of an existing product, it's crucial to identify areas for enhancement while maintaining continuity with the existing user base.
When adding a new feature to an existing product, it's essential to consider its impact on the overall user experience and ensure seamless integration with existing functionality.
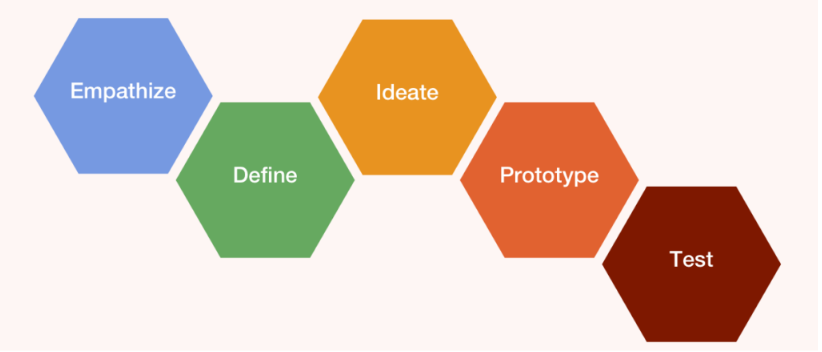
The 5 Steps:
- Empathize: Understand users' perspectives, needs, and challenges through observation, interviews, and other research methods.
- Define: Synthesize insights gathered during the empathy phase to define the core problems and opportunities that need to be addressed.
- Ideate: Encourage brainstorming and creative problem-solving by coming up with a wide range of original solutions for the given difficulties.
- Prototype: Build rough prototypes of potential solutions to visualize and test ideas, allowing for rapid iteration and refinement.
- Test: Gather feedback from users by testing prototypes, refining solutions based on insights, and iterating until an optimal solution is achieved.
Empathize
In the Empathize stage of the design thinking process, the focus is on deeply understanding the user, their emotions, and psychological needs. This involves immersing oneself in the user's world to gain empathy and insight into their experiences, challenges, and aspirations. By engaging with users directly, observing their behaviors, and actively listening to their stories and feedback, designers can uncover latent needs and desires. Additionally, understanding the industry landscape, competitors, and similar products provides context and benchmarks for innovation. Empathy serves as the foundation for meaningful problem-solving, enabling designers to develop solutions that resonate with users on a profound level and ultimately lead to more impactful and user-centered design outcomes.
Here are some methods to empathize with users:
- Observation: To learn how users engage with products or services, observe their behavior.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews with users to delve deeper into their experiences, preferences, and pain points.
- Surveys: Use surveys to gather quantitative data about users' needs and behaviors.
- Empathy Maps: Create empathy maps to visually represent users' thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Define
The Define stage is about synthesizing the insights gathered during the Empathize stage to define the core problems and opportunities. This stage is crucial for framing the design challenge effectively. The Define mode is essential to the design process because it produces your point-of-view (POV), which is the clear statement of the issue you are attempting to solve. More crucially, your point of view, grounded in your newfound comprehension of people and the problem domain, identifies the RIGHT challenge to take on. While creating a more specific problem statement tends to provide more high-quality and higher-quantity solutions throughout the ideation process, it may appear paradoxical.
Methods for defining the problem include:
- Problem Statements: Craft clear and concise problem statements based on user insights to guide the design process.
- User Personas: Develop personas that represent the key user segments and their specific needs and goals.
- Journey Mapping: Map out the user journey to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Ideate
The Ideate stage is all about generating creative solutions to address the defined problems. It's a divergent phase where teams brainstorm ideas without judgment.To get from problem identification to solution creation for your users, you ideate. Ideation is the process of combining your imagination with your knowledge of the problem domain and the target audience to produce potential solutions.
Here are some ideation methods:
- Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a group activity where people come together to share ideas and think creatively to solve problems.
- Sketching: Use sketching as a visual tool to explore and communicate ideas quickly.
- Mind Mapping: Create mind maps to visually organize and connect different concepts and ideas.
- Reverse Thinking: Challenge assumptions by thinking about the problem from unconventional perspectives.
Prototype
In the Prototype stage, teams transform ideas generated during ideation into tangible solutions. This involves prototyping and iterating on designs to refine them further. The prototyping phase involves creating representations of the ideas generated during the ideation phase. Prototyping serves several purposes:
- Visualizing Ideas: Prototypes can be sketches, diagrams, storyboards, or physical models that help visualize concepts.
- Testing Concepts: Prototypes allow you to quickly test ideas and gather feedback before investing significant time and resources. This helps in identifying potential flaws, improvements, or new insights early in the process.
- Iterating Solutions: Through prototyping, you can refine and iterate on different solutions based on user feedback and insights gathered during testing.
Methods for designing solutions include:
- Prototyping: Create low-fidelity prototypes to test and validate design concepts early in the process. Iterate on prototypes based on user feedback.
- Storyboarding: Use storyboarding to visualize user interactions with the proposed solution in a sequential manner.
- Wireframing: Develop wireframes to outline the structure and layout of digital interfaces.
- Mockups: Design high-fidelity mockups to showcase the visual design and user interface elements of the solution.
Test
The Test stage is about gathering feedback from users to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed solutions. Testing helps identify strengths and weaknesses and informs further iterations.The goal is to gain a deep understanding of the users and their ideal solution/product.
Methods for testing solutions include:
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability tests to observe how users interact with the solution and identify any usability issues.
- Prototype Testing: Test prototypes with real users to gather feedback on the overall user experience and specific features.
- A/B Testing: Compare different versions of the solution to determine which design performs better in terms of user engagement and satisfaction.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops to continuously gather input from users and stakeholders throughout the design process.