Cloud-based quality assurance (QA)

Cloud-based quality assurance (QA) is increasingly replacing traditional on-premises QA due to its ability to save time and costs, streamline testing processes, and provide access to a broader range of devices.
What is Cloud-based Testing?
Cloud-based testing is a QA method that uses cloud-based tools to simulate real-world user activity and environments, helping to test applications, networks, and infrastructure.
Cloud-based testing providers offer customizable testing environments that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of an application. They provide cloud-based testing labs, services for managing these labs, service virtualization, on-demand testing tools, and device clouds. The ease of adopting these tools and the variety of available solutions are driving the growing adoption of cloud-based QA.
Main Types of Cloud Testing
In a cloud environment, there are several types of testing that can be performed:
- Functional Testing focuses on ensuring that the software’s features and functions work as expected and that it interacts correctly with hardware. This includes system testing, acceptance testing, and integration testing. Popular tools for functional testing include QAwerk, Rapise, and Sauce Labs.
- Non-functional Testing evaluates aspects of the software that go beyond functionality, such as performance, usability, and reliability. This type of testing is typically divided into three main categories: testing for business requirements, security, and scalability/performance. Tools like AppPerfect, Nmap, Nessus, and Wireshark are commonly used for non-functional testing.
- Ability Testing checks whether the application can deliver services on demand from the cloud environment. This involves testing for compatibility, operability, disaster recovery, and multi-tenancy. Tools such as ClickTest, BrowserStack, and Quorum are often used for these tasks.
Types and Models of Cloud-based Testing Tools
When choosing a cloud-based testing tool or service, it's important to consider several key factors:
- Tenancy Mode: Cloud-based testing solutions can be either single-tenant or multi-tenant. Single-tenant solutions are dedicated to one client, while multi-tenant solutions allow multiple clients to share the same instance. Multi-tenant options are generally more cost-effective, but single-tenant solutions offer better security, which is essential for sensitive data.
- Deployment Type: There are three main deployment options for cloud-based testing: public, private, and hybrid. Public deployments are the most common due to their ease of use and scalability. Private and hybrid deployments offer higher security but can be more complex to set up. Additionally, not all cloud-based testing tools support private deployment options.
- Service Model: Cloud-based testing services are available in different models, including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Each model provides different levels of control, responsibility, and maintenance, allowing you to choose the one that best suits your testing needs.
Benefits of cloud-based testing
In contrast to traditional software testing, cloud-based testing has several unique advantages:
- Scalable — Cloud computing allows testers to increase or decrease computing resources fast. This is useful in cases when the customer frequently changes their business requirements.
- Cost efficiency — In cloud computing, you pay only for the resources you use. This means there’s no need to invest in purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading expensive equipment. You can have all the software and hardware you might need at your disposal while only paying for it when you actually use it.
- Properly configured test environment — It usually takes much time to properly set up a test environment on multiple devices. Moreover, any errors made during environment configuration can be repeated across all devices. Fortunately, you can avoid this by using cloud-based tools that have been preconfigured by their provider, saving your time and money. You can also combine various testing environments and customize them to achieve the best possible result.
- Comprehensive — In order to conduct comprehensive testing, the test team needs to run an application on all possible devices that support different platforms, operating systems, and browsers. Cloud-based testing provides you with all these devices and configurations, eliminating the need to purchase all of them.
- Improved team collaboration — Cloud-based testing allows software companies to include DevOps in their workflows because it requires collaboration between developers and testers. In the cloud, testers can spin up test environments with different configurations and data, automate testing processes, integrate with development tools to provide feedback fast, and get help from DevOps in setting up tools.
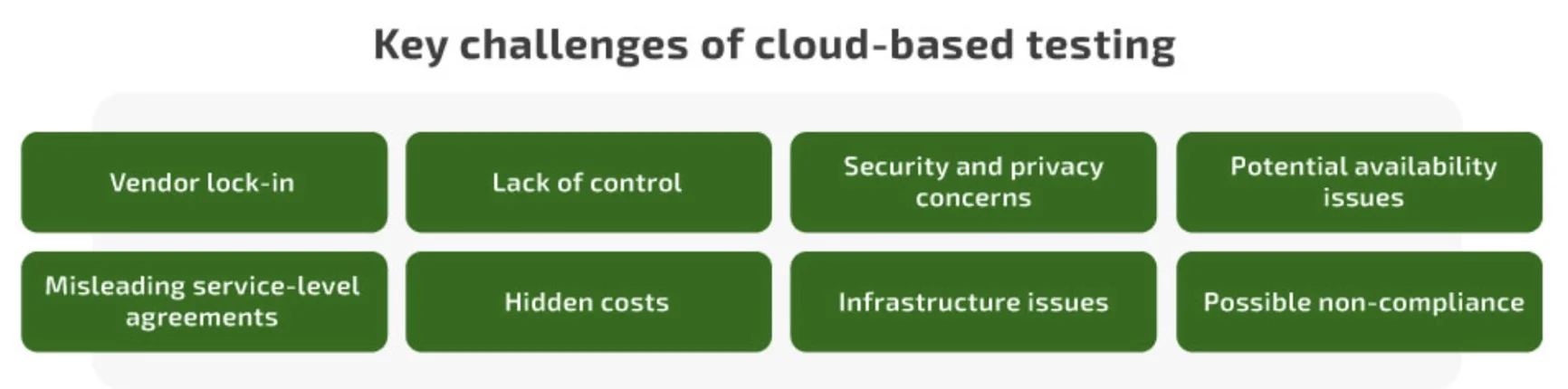
Key cloud testing challenges
Cloud-based testing also has several challenges you should consider before adopting this practice. Let’s look closely at operational challenges QA specialists should be ready to overcome:
Conclusion
Cloud-based testing offers organizations a way to reduce both the costs and time spent on software testing. However, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and challenges before making the switch to cloud-based testing.
QA teams can transition more smoothly by understanding the different types of cloud-based testing and gaining experience with cloud-based tools and environments. At Apriorit, we have a team of experienced QA specialists ready to assist you with cloud-based testing services. Contact us to discuss how we can support your project!